Understanding Viral Infections: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention
“Understanding the Basics of Viral Infections: Exploring the Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention Strategies. Stay informed and protect yourself from viral infections with our comprehensive guide.”
Understanding Viral Infections: What You Need to Know
A viral infection is a type of infectious disease caused by a virus. These infections are usually transmitted from person to person, but they can also be spread through animal bites or contact with contaminated objects. Viruses are microscopic organisms that are smaller than bacteria. They consist of genetic material (DNA or RNA) and a protein coat. Unlike bacteria, viruses are parasites and cannot survive without a host, such as humans, animals, or plants. When a virus infects a host cell, it reproduces and kills the host cell. Viruses can attack various tissues or organs in the body, such as the respiratory or digestive system. However, not all viruses that enter the body cause illness because a healthy immune system can fight off the virus.
Types of Viral Infections
- Respiratory infections: These infections affect the upper or lower respiratory system. They can affect organs like the nose, sinuses, throat, and lungs. Respiratory viruses are primarily transmitted through respiratory droplets from coughing or sneezing.
- Gastrointestinal infections: These infections affect organs in the digestive system like the stomach and intestines. Gastrointestinal viruses spread through contaminated food or water, as well as poor hand hygiene after using the bathroom.
Risk Factors for Viral Infections
- Elderly individuals or children
- Poor nutrition or malnutrition
- Unprotected sexual activity with multiple partners
- Frequent changes in sexual partners
How Do Viral Infections Spread? Exploring Transmission Methods
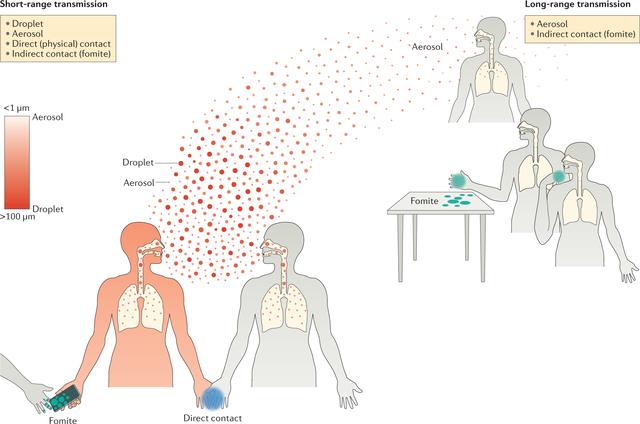
Viral infections can spread through various methods, depending on the specific virus. The most common modes of transmission include:
Respiratory Droplets
Many respiratory viruses, such as the flu or common cold viruses, spread through respiratory droplets generated when an infected person coughs or sneezes. These droplets can be inhaled by nearby individuals, leading to infection.
Direct Contact
Some viruses can spread through direct contact with infected bodily fluids or surfaces contaminated with these fluids. Examples include herpes simplex virus (HSV), which can be transmitted through kissing or sexual contact, and hepatitis B and C viruses, which can be transmitted through sharing needles or other drug paraphernalia.
Ingestion of Contaminated Food or Water
Gastrointestinal viruses like norovirus and rotavirus can be contracted by consuming food or water that has been contaminated with the virus. Poor food handling practices and unsanitary conditions contribute to the spread of these infections.
Recognizing the Symptoms: Common Signs of a Viral Infection
The symptoms of a viral infection can vary depending on the specific virus and organ system affected. Some common symptoms include:
- Fever
- Coughing
- Sore throat
- Nasal congestion
- Vomiting or diarrhea (gastrointestinal infections)
- Rash (skin infections)
When to See a Doctor
If you experience persistent fever above 39°C (102°F) or develop severe symptoms such as chest pain, abdominal pain, neck stiffness, confusion, or loss of consciousness, it is important to seek medical attention promptly.
Diagnosing Viral Infections: Methods and Procedures

To diagnose a viral infection, your doctor will typically ask about your symptoms and medical history. They will also perform a thorough physical examination. In some cases, further testing may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis. Common diagnostic methods include:
- C-reactive protein (CRP) test: Measures the level of C-reactive protein in the blood, which indicates inflammation.
- Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA): Detects specific antibodies in the blood that are associated with certain viral infections.
- Electron microscopy: Examines blood or tissue samples under an electron microscope to identify viral particles.
In some instances, a culture may be performed to distinguish between viral and bacterial infections. This involves collecting a sample of blood or urine for laboratory analysis. A biopsy may also be performed to examine infected tissues under a microscope.
Treatment Options for Viral Infections: What Are Your Choices?
The treatment of viral infections depends on the specific virus involved. In many cases, viral infections such as respiratory or gastrointestinal infections resolve on their own without specific antiviral treatment. However, your doctor may prescribe medications to manage symptoms such as nausea, diarrhea, fever, or pain. In certain cases, antiviral medications can be used for specific viral infections like influenza (flu), herpes, or HIV.
Common Treatment Approaches
- Antiemetics: Medications used to relieve nausea and vomiting.
- Loperamide: A medication that helps treat diarrhea by slowing down intestinal movement.
- Paracetamol and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Used to reduce fever and alleviate pain.
Preventing Viral Infections: Effective Strategies to Stay Healthy
Preventing viral infections involves implementing good hygiene practices and taking necessary precautions:
- Cook food thoroughly to kill any potential viral pathogens.
- Avoid close contact with infected individuals and contaminated surfaces.
- Practice safe sex by using condoms and limiting the number of sexual partners.
- Get vaccinated against viruses such as influenza, hepatitis, HPV, and others.
- Wash hands frequently with soap and water for at least 20 seconds.
Potential Complications of Viral Infections: Understanding the Risks
Viral infections can lead to various complications depending on the virus and individual factors. Some potential complications include:
- Chronic hepatitis or liver cirrhosis from hepatitis B, C, or D infections
- Cervical cancer due to human papillomavirus (HPV) infection
- Asthma exacerbation or bronchiolitis from respiratory viral infections
In some cases, a weakened immune system may fail to effectively combat a viral infection. This can result in serious complications such as certain types of cancers, birth defects in infants, or viral hemorrhagic fevers.
In conclusion, viral infections are a common occurrence caused by various types of viruses. They can spread rapidly and affect individuals of all ages. It is important to practice good hygiene, such as regular handwashing, to prevent the spread of viral infections. Additionally, vaccination plays a crucial role in protecting against certain viral infections. Proper medical care and following healthcare guidelines are essential for managing symptoms and preventing complications related to viral infections.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gm8EW-gfgKs&pp=ygUWdmlyYWwgaW5mZWN0aW9uIGFkYWxhaA%3D%3D
