Recognizing the Symptoms of Viral Bronchitis: What You Need to Know
“Unraveling Viral Bronchitis Symptoms: A Guide to Identifying and Managing This Common Respiratory Condition. Understand the telltale signs, treatment options, and preventive measures in this comprehensive overview of viral bronchitis symptoms.”
Common Symptoms of Viral Bronchitis
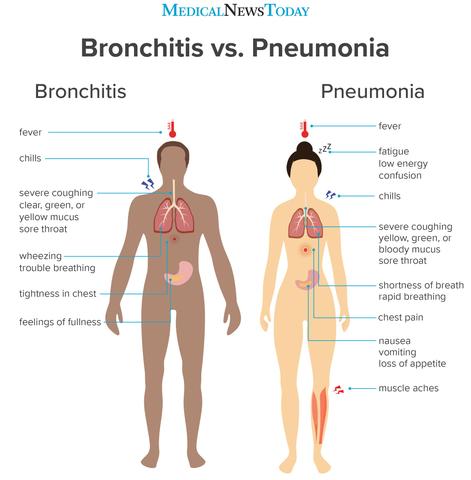
Viral bronchitis is an inflammation of the airways called bronchi, which is caused by a viral infection. The most common symptoms of viral bronchitis include a persistent cough that may start off dry and non-productive but later produces mucus, chest soreness, runny nose, fatigue and achiness, headache, chills, slight fever, and sore throat. These symptoms are similar to those of a common cold or the flu.
In addition to these symptoms, some individuals with viral bronchitis may also experience wheezing or difficulty breathing due to the inflammation in the airways. This can be particularly worrisome for individuals with pre-existing lung conditions such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
It’s important to note that viral bronchitis typically does not cause fever higher than 100.4°F (38°C) and does not result in severe shortness of breath or chest pain. If you experience these more severe symptoms or if your symptoms worsen over time despite appropriate self-care measures, it is recommended to seek medical attention.
Common Symptoms:
- Persistent cough
- Chest soreness
- Runny nose
- Fatigue and achiness
- Headache
- Chills
- Slight fever
- Sore throat
Duration of Symptoms in Viral Bronchitis
The duration of symptoms in viral bronchitis can vary from person to person but generally resolves within two weeks. However, the cough associated with viral bronchitis can persist for up to eight weeks in some individuals. It’s important to note that the cough may last longer in individuals who have pre-existing lung conditions or compromised immune systems.
During the first week of viral bronchitis, symptoms may be more intense and may include a non-productive cough, sore throat, and mild fever. As the infection progresses, the cough may become productive and phlegm or mucus may be coughed up. Fatigue and chest discomfort may also persist during this time.
If symptoms worsen after two weeks or if new symptoms develop, it is recommended to seek medical attention as it could indicate a secondary infection or complications. It’s also important to monitor your symptoms closely if you have a pre-existing lung condition or other underlying health issues.
Duration of Symptoms:
- Generally resolves within two weeks
- Cough can persist for up to eight weeks
- Symptoms may be more intense during the first week of infection
- If symptoms worsen after two weeks or new symptoms develop, seek medical attention
Possible Complications and Progression of Viral Bronchitis
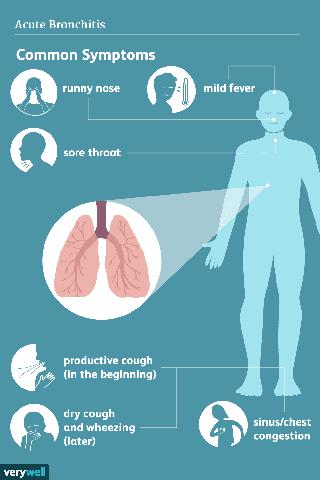
Viral bronchitis can sometimes lead to complications or progress to a more serious condition. One possible complication is the development of pneumonia. Pneumonia is an infection that causes inflammation in the air sacs of the lungs. It can be particularly dangerous for those with weakened immune systems or underlying lung conditions.
Another complication of viral bronchitis is exacerbation of asthma symptoms. If you already have asthma, a respiratory infection like viral bronchitis can trigger an asthma attack, resulting in wheezing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness.
In some cases, viral bronchitis may also lead to chronic bronchitis. Chronic bronchitis is a long-term condition characterized by persistent cough and excessive mucus production for at least three months out of the year for two consecutive years. It can significantly impact a person’s quality of life and may require ongoing management and treatment.
Prevention Strategies:
– Wash your hands frequently with soap and water to reduce the risk of contracting viral infections.
– Avoid close contact with individuals who have flu-like symptoms or respiratory infections.
– Get vaccinated against common viruses such as influenza.
– Practice good respiratory hygiene by covering your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing, preferably with a tissue or your elbow.
– Avoid smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke, as it can increase your susceptibility to respiratory infections.
Early Intervention:
If you notice any worsening symptoms or experience difficulty breathing, it is important to seek medical attention promptly. Early intervention can help prevent complications and ensure appropriate treatment for viral bronchitis. Contact your healthcare provider if you develop high fever, severe chest pain, persistent cough with bloody phlegm, or if your symptoms do not improve after a week.
Diagnosis of Viral Bronchitis and Confirming the Infection
Diagnosing viral bronchitis involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and sometimes additional tests. Your healthcare provider will start by asking about your symptoms and conducting a thorough evaluation of your respiratory system.
During the physical exam, they may listen to your lungs with a stethoscope to assess for abnormal sounds such as wheezes or crackles. They will also check for signs of congestion or inflammation in your nasal passages and throat.
In order to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other potential causes, your healthcare provider might recommend certain tests:
Chest X-ray:
A chest X-ray can help evaluate the condition of your lungs and exclude other respiratory conditions such as pneumonia. It can reveal any abnormalities or signs of infection that may be contributing to your symptoms.
Lab Tests:
A sputum culture or nasal discharge sample may be collected to identify the specific virus causing the infection. This can help determine if your bronchitis is caused by a viral pathogen rather than bacteria.
Pulmonary Function Tests:
These tests assess how well your lungs are functioning and measure factors like lung capacity, airflow, and gas exchange. They can provide valuable information on the severity of bronchial inflammation and help guide treatment decisions.
Treatment Recommendations for Viral Bronchitis: Antibiotics?
Most cases of viral bronchitis resolve on their own without specific treatment. Since antibiotics are only effective against bacterial infections, they are not typically prescribed for viral bronchitis. However, there are various treatment recommendations aimed at managing the symptoms and supporting recovery:
Symptom Relief:
– Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen (Tylenol) or ibuprofen (Advil) can help reduce fever, ease discomfort, and relieve chest soreness.
– Cough suppressants may be used to alleviate a persistent cough that disrupts sleep or daily activities. However, it is important to note that coughing plays a role in clearing mucus from the airways, so suppressing it completely may impede healing.
– Drinking plenty of fluids can help thin out mucus and ease congestion. Warm liquids, such as herbal teas or broths, might provide additional relief.
– Using a humidifier or taking steamy showers can help moisten the airways and alleviate dry cough.
Rest and Self-Care:
Ensuring an adequate amount of rest is crucial for allowing your body to recover. Avoid strenuous activities and get plenty of sleep.
Avoiding Irritants:
It is essential to avoid exposure to irritants that can further exacerbate respiratory symptoms. This includes cigarette smoke, strong fumes, environmental pollutants, and allergens.
While there isn’t a specific antiviral medication available for viral bronchitis, your healthcare provider might prescribe antiviral drugs if you have a high risk of complications or a confirmed influenza infection.
Remember to consult with your healthcare provider before taking any over-the-counter medications or using home remedies to ensure they are appropriate for your specific situation. They can provide personalized guidance based on the severity of your symptoms and overall health status.
Preventive Measures and Vaccinations for Viral Bronchitis
Taking preventive measures is key in reducing the risk of contracting viral bronchitis. There are several strategies you can adopt to protect yourself and others:
Vaccinations:
Getting vaccinated against common viruses like influenza (flu) and pneumonia can significantly lower your chances of developing viral bronchitis. The flu shot should be received annually since the flu virus undergoes frequent changes.
Additionally, older adults or individuals with certain medical conditions, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), may benefit from the pneumococcal vaccine. This vaccine protects against a type of bacteria that commonly causes pneumonia.
Hand Hygiene:
Regular handwashing with soap and water is one of the most effective ways to prevent the spread of respiratory infections. Make sure to scrub your hands thoroughly for at least 20 seconds, especially after coughing, sneezing, or touching surfaces in public places.
If soap and water are not readily available, use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer containing at least 60% alcohol.
Cover Your Mouth and Nose:
When coughing or sneezing, cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or your elbow. This helps prevent the spread of respiratory droplets that can contain viruses. Dispose of used tissues appropriately and wash your hands afterwards.
Avoid Close Contact:
Avoid close contact with individuals who have flu-like symptoms or respiratory infections. Viral bronchitis is highly contagious, primarily through respiratory droplets produced when an infected person coughs or sneezes.
Additionally, try to avoid crowded places during peak flu seasons to reduce your exposure to potential sources of infection.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Viral Bronchitis Symptoms
In most cases, viral bronchitis resolves on its own within a couple of weeks without any serious complications. However, there are situations where seeking medical attention is necessary:
Worsening Symptoms:
If your symptoms worsen or persist for more than two weeks without improvement, it is advisable to consult your healthcare provider. They can evaluate your condition and determine if there are any underlying factors contributing to the prolonged symptoms.
High Fever:
If you experience a high fever (above 100.4°F or 38°C) that does not respond to over-the-counter fever reducers, it is important to seek medical attention. High fevers can indicate a more severe infection or pneumonia.
Difficulty Breathing:
If you have difficulty breathing, experience shortness of breath at rest, or find it hard to complete simple tasks due to breathlessness, it is crucial to seek immediate medical care. These symptoms may indicate a respiratory emergency and require prompt evaluation and treatment.
Inability to Drink Fluids:
If you are unable to drink fluids due to severe throat pain, persistent vomiting, or inability to keep fluids down, contact your healthcare provider. Dehydration can worsen your overall condition and may require intervention.
Remember, it is always better to err on the side of caution when it comes to your health. If you have any concerns about your symptoms or if they are causing significant distress, do not hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider for guidance.
In conclusion, viral bronchitis symptoms can range from mild to severe and may include coughing, wheezing, chest congestion, and fatigue. While most cases resolve on their own with rest and fluids, it is important to seek medical attention if symptoms worsen or persist. Taking preventive measures such as practicing good hygiene and getting vaccinated can help reduce the risk of contracting viral bronchitis.
